
A drug is any substance (with the exception of food and water) which, when consumed, changes the body's function either physically and/or psychologically. Drugs can be identified as legal (eg alcohol, caffeine and tobacco) or illegal (e.g. cannabis, ecstasy, cocaine and heroin).
Drugs are anything (except food and water) which, if eaten, alters physical activity can be physical and / or mental. Drugs can be identified as legal (eg alcohol, caffeine and tobacco) or illegal (eg marijuana, ecstasy, cocaine and heroine).
Drug abuse problems can be seen as less harmful than drug addiction. Or, continued use of illegal substances can also harm the user's health.
• Legal problems caused by substance abuse or behavior under the influence of
• Physical harm to others caused by individual drug use and/or behavior under the influence
(or absence of action due to drug use)
• Failure to do what is required at home, school, work, or general administration.
• Continued drug use despite ongoing problems in these and other areas caused by substance abuse

• The onset of withdrawal symptoms (physical and mental) if you do not have the drug of your choice.
• More and larger doses of the drug of your choice are used to achieve the same results at first.
• Less interest in past hobbies and interests or work/school activities.
• Withdrawal from friends and family.
• Behavioral patterns focus only on finding or staying on top.
• Many attempts to reduce or stop drug use without success.
• Continuing drug and alcohol use despite the ongoing and growing problems associated with its use.
"It will be difficult before it is easy. But it will be better. You just have to do it through. "
Drugs can be categorized on the basis of chemical reactions, the legal system of countries, effects of drugs.
Alcohol is a very addictive substance. Alcohol creates feelings of happiness and less self-control, but also more disrupts judgment, understanding, and response times. Alcohol is a stressful central nervous system, however it causes liver damage for a very long time. Alcohol can be obtained in the form of beer, wine or Alcohol.
Opioids work in conjunction with neurotransmitters in the brain and inhibit signals sending. This makes opioids work as powerful painkillers, but can also create feelings of dizziness happiness, which leads to addiction. Opioids are usually available in the form of Heroin, Fentanyl or Oxycodone.
Benzodiazepines work in conjunction with the neurotransmitter gamma-aminobutyric acid-A (GABA-A). Each one Benzo interacts with GABA-A differently, which is why each Benzo affects the body and mind differently. Benzos are prescribed for the treatment of various psychiatric and sleep disorders. Examples of Benzodiazepines are Ativan, Valium and Xanax.
Cannabinoids are chemical-like such as tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), an active agent of marijuana. Cannabinoids create a feeling of happiness, known as superior, but they also have a negative psychological effect and physical activity. Cannabinoids are the most commonly abused drugs after alcohol, and they are increasingly popular gaining legal recognition. Examples of cannabinoids are Marijuana and Hashish.
Barbiturates work on the central nervous system by reducing its effectiveness. Barbiturates are derived from barbituric acid. Barbiturates were historically known for their mental and sleep disorders, and are still used for anesthesia and numerical treatment conditions such as epilepsy and headache. Examples of Barbiturates are Amytal, Luminal and Pentobarbita.
Stressors create feelings of rest and fatigue. While many serve for legitimate purposes in war against mental illness and deprivation of sleep, they are often severely abused because they can also cause it feelings of happiness. Depressors include Alcohol, Opioids and Barbiturates.
Incentives are used to increase energy, focus, and alertness or to increase productivity as well performance. Examples of incentives include Adderall, Cocaine and Meth.
Hallucinogens alters the user's perception of reality, which often leads to misunderstanding and perception madness. Examples of Hallucinogens include LSD, Philocybin Mushroom and PCP.
Inhalants are a variety of chemicals that are injected primarily through respiration. While inclined to be less addictive than most other things, the use of inhalants is incredibly dangerous. Examples of inhalants include Paint Thinner, Nail Polish Remover and gasoline.

Drug abuse can have both short and long lasting effects on the consumer.
● changes in appetite
● sleeplessness or insomnia
● increased heart rate
● slurred speech
● changes in cognitive ability
● a temporary sense of euphoria
● loss of coordination
● an inability to cease using a drug relationship problems
● poor work or academic performance
● difficulty maintaining personal hygiene
● noticeable changes in appearance, such as extreme weight loss
● increased impulsivity and risk-taking behaviors
● loss of interest in formerly enjoyable activities
● depression
● anxiety
● panic disorders
● increased aggression
● paranoia
● hallucinations
● It can also effect consumer's memory, learning, and concentration
● Drug dependence. Teens who misuse drugs are at increased risk of serious drug use later in life.
● Poor judgment. Teenage drug use is associated with poor judgment in social and
personal interactions.
● Sexual activity. Drug use is associated with high-risk sexual activity, unsafe sex and unplanned
pregnancy.
● Mental health disorders Drug use can complicate or increase the risk of mental health disorders,
such as depression and anxiety.
● Impaired driving Driving under the influence of any drug can impair a driver's motor
skills, putting the driver, passengers and others on the road at risk.
● Changes in school performance. Substance use can result in a decline in academic performance.
● A family history of substance abuse
● A mental or behavioral health condition, such as depression, anxiety or attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD)
● Impulsive or risk-taking behavior
● A history of traumatic events, such as experiencing a car accident or being a victim of abuse
● Low self-esteem or feelings of social rejection
The Narcotics Control Bureau is an Indian Federal Law enforcing and intelligence agency under the Department of Department of Home Affairs, Government of India. The organization is tasked with combating drug trafficking and the use of illicit drugs items subject to the provisions of the Narcotic Drugs and the Psychotropic Substances Act.

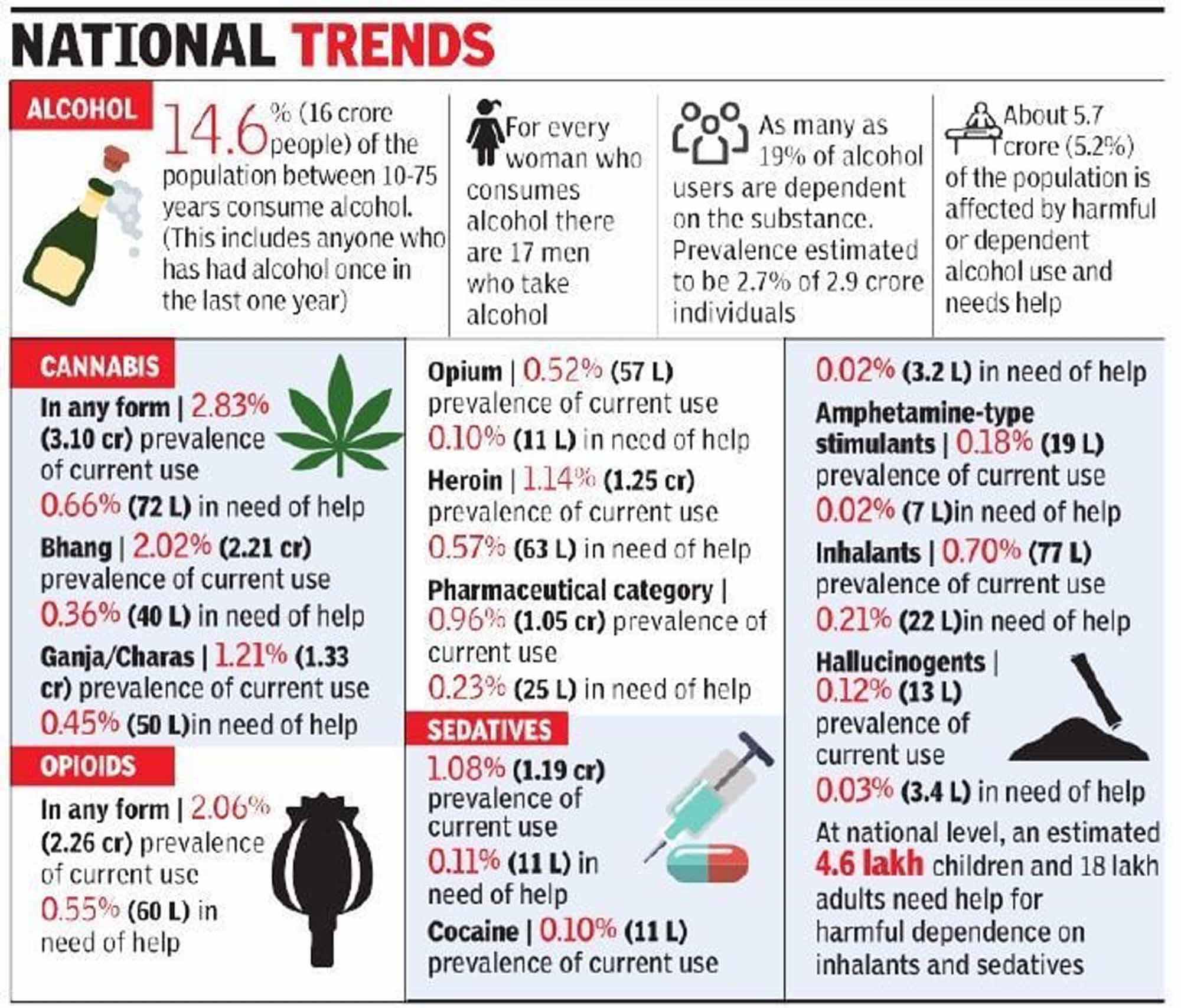
the Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment (MoSJE), Government of India, commissioned a National Survey on Extent and Pattern for Substance Use in India.
As mentioned earlier, drug prevention begins with education. This education can be done by number
levels include:
● Prevention of Family-Based Drugs.
Prevention of drug abuse should begin within the family as
early. There are many obvious benefits to home-based drug prevention education including
self-awareness, and improving parent-child communication skills and family bonding. Parental
surveillance and involvement are very important for young people. Parents need to do more than just teach
children at risk of drug abuse and abuse, but they must also establish and enforce family rules. This
including creating an effective system to monitor their children's activities.
● School Harassment Prevention Programs.
Prevention of drug abuse must be addressed early
kindergarten. Kindergarten children can benefit by learning how to deal with anger, problem-solving, and
better communication so that they can avoid putting themselves at risk of drug abuse later in life. In the middle
and high school programs should focus on peer relations, communication, confidence, drug resistance
skills and developing anti-drug strategies. Security plans for the school should be repeated several times in the files of
a good level of success.
● Community-Based Community Violence Prevention Programs.
Communities making efforts to unite
in the fight against drugs it will inevitably contribute to preventing drug abuse. There are many places
establishing these protection programs includes schools, churches and community clubs.
Change must start from the individual. And the individual must want and feel ready to make such change.”
– Efrat Cybulkiewicz
1800-11-0031
● Consult Government Helpline or Councillor
● Reduce Intensity And Try To Slow And Steadily Switch To Healthy Alternatives - Cultivate Strong Will
● Join Support Group
● Rehabilitation
● Avoid Company Of Drug Addicts - Seek Positive Friends
● Get Involved In Activities

Mental health includes our emotional, psychological, and social well-being. It also helps determine how we handle stress, and make choices.

Awareness about this issue should be encouraged to not only prevent it but also to help out the victims in getting their lives back.

Now turn that frown upside down … even if it means standing on your head.
Just smile and enjoy the beauty
of life.